Decentralization is one of those words people throw around like everyone already understands it. It shows up in crypto whitepapers, political debates, startup pitches, and philosophy podcasts. It sounds futuristic, maybe even radical. But when you strip away the hype, decentralization isn’t an abstract idea or a technical trick.
It’s something humans have been doing — imperfectly, creatively, and sometimes accidentally — for thousands of years.
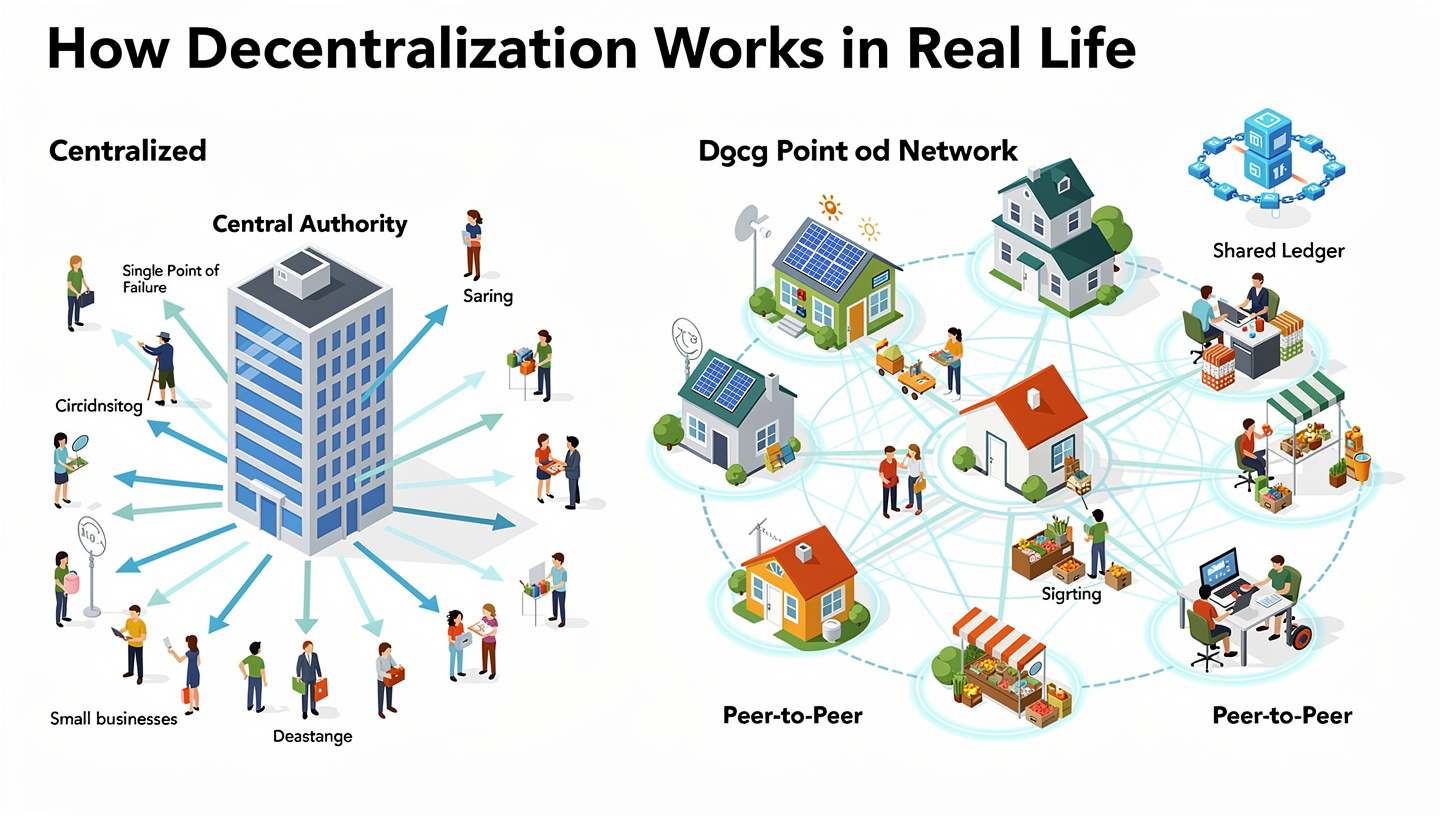
Decentralization is not about removing structure.
It’s about removing the single point of control.
And once you see how it works in real life, you start noticing it everywhere.
1. Centralization vs. Decentralization: A Human Problem, Not a Tech One
Before computers, blockchains, or the internet existed, societies already faced a fundamental question:
Who gets to decide?
Centralization answers: a small group, a single authority, a trusted middleman.
Decentralization answers: many participants, shared rules, distributed power.
Neither is inherently good or evil. Centralization can be efficient. Decentralization can be messy. The tension between the two has shaped empires, religions, markets, and cultures long before code entered the picture.
A Simple Mental Model
- Centralized system:
One brain, many hands. - Decentralized system:
Many brains, shared rules.
The magic — and the challenge — lies in how those shared rules are enforced without a single boss.
2. Decentralization in Nature: The Oldest Example We Ignore
If you want to understand decentralization in real life, stop looking at technology for a moment. Look at nature.
Ant Colonies: No CEO, No Chaos
Ant colonies don’t have a central command ant telling everyone what to do. No ant has the full picture. Yet colonies:
- Build complex structures
- Allocate labor efficiently
- Adapt to threats
- Survive massive disruptions
How?
Each ant follows simple local rules, reacting only to nearby information (pheromones, obstacles, signals). Intelligence emerges from the network.
That’s decentralization in its purest form:
- No single point of failure
- No master plan
- Order emerging from participation
Sound familiar?
3. Language: A Decentralized System You Use Every Day
No one invented English.
No committee controls Vietnamese.
No global authority approves slang.
Language evolves because millions of people agree implicitly on meanings over time.
- Words gain power through usage, not permission
- Grammar bends when enough people bend it
- New expressions spread peer-to-peer
If language were centralized, every new word would need approval. Creativity would die. Culture would freeze.
Instead, language thrives because it’s decentralized — coordinated by shared understanding, not enforced authority.
4. Money Before Banks: Trust Without Institutions
Long before central banks and modern finance, humans traded value using decentralized systems.
- Shells
- Salt
- Gold
- Beads
- Livestock
These worked because:
- No single entity controlled supply
- Value emerged from shared belief
- Verification was social, not institutional
Gold didn’t need a CEO.
It didn’t need a server.
It needed collective trust.
This is why crypto didn’t invent decentralization — it rediscovered it, then automated it.
5. The Internet Itself Is Decentralized (Mostly)
The internet was designed to survive catastrophe.
Instead of one central server connecting everyone, it uses:
- Distributed routing
- Redundant pathways
- Independent networks
If one node goes down, traffic reroutes.
If one country blocks access, others still function.
This design wasn’t ideological — it was practical. Decentralization meant resilience.
Ironically, many modern internet services re-centralized on top of this decentralized foundation (social media platforms, cloud providers). The base layer remains decentralized; the user experience often isn’t.
This tension defines our digital age.
6. Decentralization in Business: When Power Moves Sideways
Open-Source Software
Linux doesn’t belong to one company.
Wikipedia doesn’t have a single author.
Bitcoin doesn’t have a CEO.
Open-source projects work because:
- Anyone can contribute
- Rules are transparent
- Consensus decides direction
- Forking is always possible
Forking is decentralization’s ultimate check-and-balance.
If you don’t like how things are run, you don’t beg — you leave and build.
That threat alone keeps power honest.
Franchises vs. Platforms
- A franchise is centralized control with distributed execution.
- A platform can be decentralized coordination with shared incentives.
Uber drivers, YouTube creators, and open marketplaces sit somewhere in between — partially decentralized labor, centralized rule-making.
True decentralization means:
- Participants own their stake
- Rules can’t change arbitrarily
- Exit is always possible without permission
7. Governance Without Kings: Decentralized Decision-Making
Decentralization doesn’t mean “no rules.”
It means rules without rulers.
Real-World Examples
- Cooperatives: One member, one vote
- Homeowners associations (when done right)
- Worker-owned companies
- DAOs (digital-native governance)
The challenge is coordination.
When everyone has a voice:
- Decisions take longer
- Conflicts surface openly
- Compromise replaces command
But the upside is legitimacy. People follow rules they helped create.
8. Blockchain: Automating Decentralized Trust
Blockchain didn’t invent decentralization.
It encoded it.
Instead of trusting people, we trust:
- Cryptography
- Mathematics
- Open verification
In real life, this means:
- You don’t ask permission to send value
- You don’t rely on a bank’s working hours
- You don’t trust a company’s promise — you verify the code
Consensus mechanisms replace managers.
Smart contracts replace middlemen.
Transparency replaces blind faith.
This is decentralization with teeth.
9. Decentralization Is Not Chaos (And Not a Utopia)
Here’s the uncomfortable truth:
Decentralization doesn’t remove problems — it redistributes responsibility.
There’s no customer support hotline for a lost private key.
There’s no authority to reverse every mistake.
There’s no one to blame but the system — and yourself.
Decentralization trades:
- Convenience for sovereignty
- Efficiency for resilience
- Speed for fairness
It’s not for everyone. And that’s okay.
Centralization still wins in emergencies, coordination-heavy tasks, and user simplicity.
The future isn’t fully decentralized.
It’s selectively decentralized.
10. Decentralization in Daily Life (You’re Already Using It)
You already live with decentralization more than you think:
- Choosing multiple income streams instead of one employer
- Learning from online communities instead of formal institutions
- Using peer reviews instead of brand authority
- Storing knowledge across tools, not one notebook
- Building networks instead of hierarchies
Even social trust is decentralizing:
- We trust people with reputation, not titles
- We follow voices, not institutions
- Influence spreads peer-to-peer
The world is quietly shifting from top-down to sideways.
11. Why Decentralization Matters Now More Than Ever
In a world of:
- Fragile supply chains
- Platform monopolies
- Algorithmic control
- Censorship and surveillance
- Institutional distrust
Decentralization is not a trend.
It’s a response.
A response to systems that grew too big to fail — and too powerful to trust.
Decentralization says:
- Power should be earned continuously, not granted once
- Systems should survive bad actors, not assume good ones
- Exit should always be possible
It’s less about technology and more about human dignity.
12. The Quiet Truth About Decentralization
Decentralization doesn’t scream.
It doesn’t market well.
It doesn’t promise perfection.
It simply whispers:
“You don’t need permission to participate.”
That idea — more than any protocol, token, or platform — is what makes decentralization revolutionary.
Not because it removes leaders.
But because it reminds us we were never meant to be powerless.
Final Thought
Decentralization works in real life the same way it always has:
Through shared rules, distributed trust, and collective responsibility.
Technology didn’t invent it.
History tested it.
The future depends on how wisely we use it.
And once you truly understand decentralization, you stop asking who’s in charge —
and start asking how the system earns your trust.